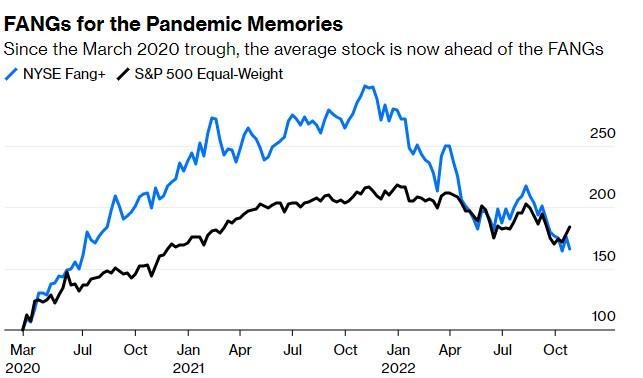
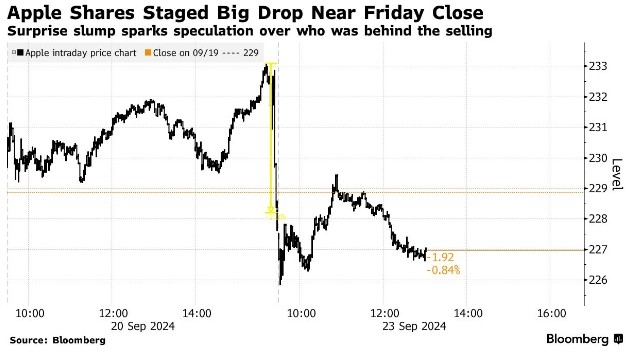
How U.S. Interest Rates Affect the Stock Market
author:US stockS -
The stock market is influenced by a myriad of factors, and one of the most significant is the interest rate set by the Federal Reserve. Understanding how these rates impact the stock market is crucial for investors looking to make informed decisions. This article delves into the relationship between U.S. interest rates and the stock market, highlighting key points and providing real-world examples.
Understanding Interest Rates

Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for individuals and businesses to borrow money. Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, borrowing becomes cheaper. This has a direct impact on the stock market.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates
When interest rates rise, several effects are observed in the stock market:
- Higher Borrowing Costs: As borrowing costs increase, companies may find it more difficult to finance their operations and expansions. This can lead to a decrease in profitability and, subsequently, a drop in stock prices.
- Bond Market Attraction: Higher interest rates make bonds more attractive to investors, as they offer higher yields compared to stocks. This can lead to a shift in investment from stocks to bonds, causing stock prices to fall.
- Consumer Spending: Higher interest rates can also lead to a decrease in consumer spending, as borrowing becomes more expensive. This can have a negative impact on companies that rely heavily on consumer demand.
Impact of Lowering Interest Rates
Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, the following effects are observed:
- Lower Borrowing Costs: Companies can borrow money at a lower cost, leading to increased investment and potentially higher profitability. This can drive stock prices up.
- Bond Market Disinterest: Lower interest rates make bonds less attractive, as they offer lower yields compared to stocks. This can lead to a shift in investment from bonds to stocks, causing stock prices to rise.
- Consumer Spending: Lower interest rates can encourage consumer spending, as borrowing becomes cheaper. This can have a positive impact on companies that rely heavily on consumer demand.
Real-World Examples
One notable example of the impact of interest rates on the stock market is the 2008 financial crisis. In response to the crisis, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to historic lows. This resulted in a significant increase in stock prices as investors sought higher returns in the stock market.
Another example is the 2015-2016 period, when the Federal Reserve raised interest rates. This led to a period of uncertainty in the stock market, with some investors concerned about the potential impact of higher borrowing costs on corporate profitability.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between U.S. interest rates and the stock market is essential for investors. By analyzing the impact of interest rate changes, investors can better position themselves to navigate the stock market's ups and downs. Whether interest rates are rising or falling, staying informed and adapting your investment strategy accordingly is key to achieving long-term success.
us stock market live