Understanding US Stock Fundamental Data: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the world of investing, fundamental analysis is a cornerstone for making informed decisions. This approach involves analyzing a company's financial statements, industry position, and other qualitative factors to determine its intrinsic value. Understanding US stock fundamental data is crucial for investors looking to make profitable investments. This article delves into the key aspects of US stock fundamental data, providing you with the knowledge to make well-informed investment choices.
Key Components of US Stock Fundamental Data
1. Financial Statements
The cornerstone of fundamental analysis is a company's financial statements. These include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Income Statement: This statement shows a company's revenues, expenses, and net income over a specific period. It helps investors assess a company's profitability and growth potential. Key metrics to analyze include revenue growth, profit margins, and earnings per share (EPS).
Balance Sheet: This statement provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It helps investors evaluate a company's financial health and solvency. Key metrics include debt-to-equity ratio, current ratio, and return on equity (ROE).
Cash Flow Statement: This statement shows how a company generates and uses cash over a specific period. It provides insights into a company's operating efficiency and liquidity. Key metrics include operating cash flow, free cash flow, and capital expenditures.
2. Valuation Metrics
Valuation metrics are used to determine a company's intrinsic value. Some common metrics include:
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: This ratio compares a company's stock price to its EPS. A lower P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a higher ratio may suggest overvaluation.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: This ratio compares a company's stock price to its book value per share. A lower P/B ratio may indicate undervaluation, while a higher ratio may suggest overvaluation.
Earnings Yield: This metric is the inverse of the P/E ratio and shows the percentage return on a company's earnings. A higher earnings yield may indicate a better investment opportunity.
3. Industry and Market Analysis
Understanding the industry and market in which a company operates is crucial for fundamental analysis. This involves evaluating the industry's growth prospects, competitive landscape, and regulatory environment.
4. Management and Corporate Governance
The quality of a company's management and corporate governance can significantly impact its performance. Investors should assess the track record, experience, and reputation of a company's management team. Additionally, examining the company's corporate governance practices can provide insights into its decision-making process and risk management.
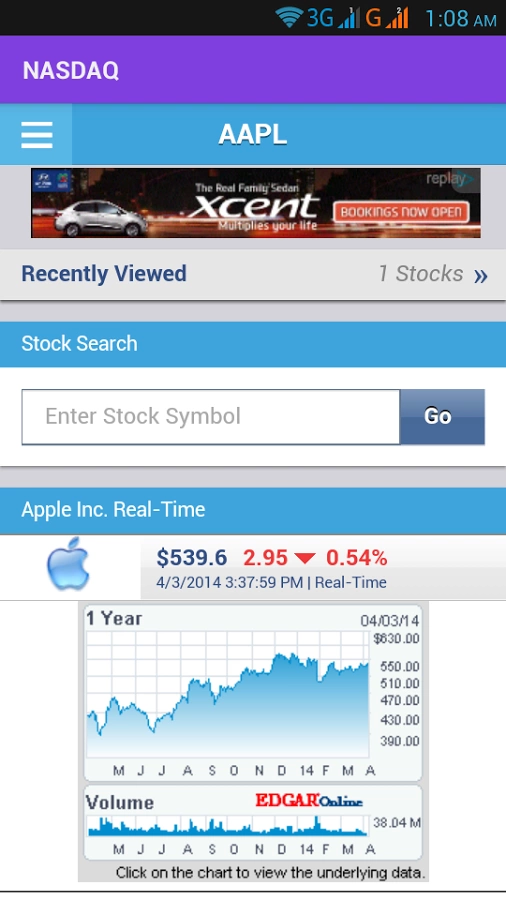
Case Study: Apple Inc.
To illustrate the importance of understanding US stock fundamental data, let's examine Apple Inc. (AAPL). Over the years, Apple has consistently delivered strong financial results, driven by its innovative products and global brand recognition. As of the latest financial statements, Apple's revenue growth, profit margins, and EPS have been impressive. The company's valuation metrics, such as P/E and P/B ratios, have historically been within reasonable ranges. Furthermore, Apple's management team and corporate governance practices have been widely praised.
In conclusion, understanding US stock fundamental data is essential for investors looking to make well-informed investment decisions. By analyzing financial statements, valuation metrics, industry and market analysis, and management and corporate governance, investors can gain valuable insights into a company's intrinsic value and potential for growth. Remember, successful investing requires thorough research and analysis, and understanding the fundamentals is the first step towards making profitable investments.
new york stock exchange