Average Standard Deviation in US Stocks: A Comprehensive Analysis
author:US stockS -
Understanding the average standard deviation of US stocks is crucial for investors who seek to gauge market volatility and manage risk. This article delves into the concept of standard deviation, its relevance in the context of US equities, and offers insights into the factors that influence it.
What is Standard Deviation?
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values. In the context of stocks, it indicates how much the returns of a particular stock deviate from its average or mean return. A higher standard deviation suggests greater volatility, while a lower standard deviation indicates lower volatility.
Average Standard Deviation of US Stocks
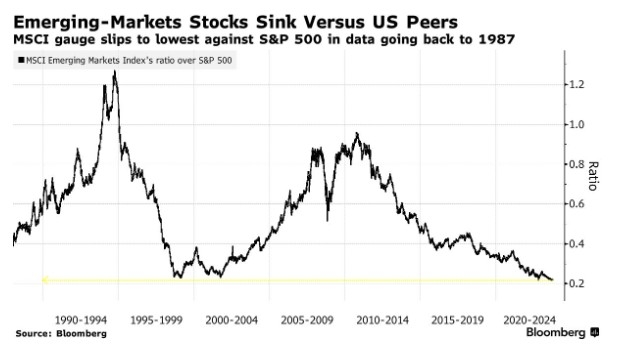
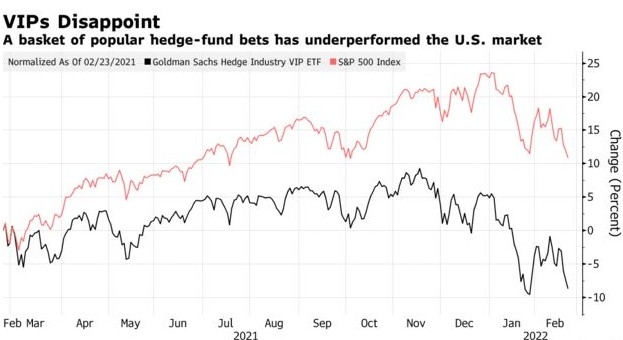
Historically, the average standard deviation of US stocks has ranged between 15% and 20%. However, this figure can vary over time, depending on market conditions, economic factors, and other variables.
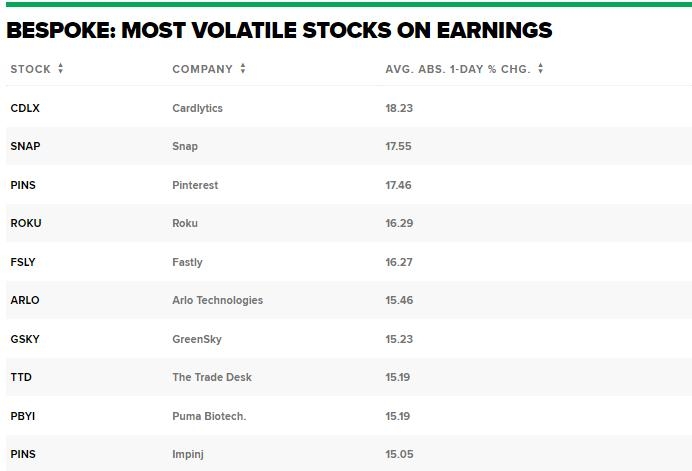
Factors Influencing Standard Deviation in US Stocks
Several factors can influence the standard deviation of US stocks:
- Market Conditions: During periods of economic uncertainty or market turmoil, such as the 2008 financial crisis or the recent COVID-19 pandemic, stock prices tend to be more volatile, leading to higher standard deviation.
- Sector and Industry: Different sectors and industries have varying levels of risk and volatility. For instance, technology stocks often exhibit higher standard deviation compared to utility stocks.
- Company-Specific Factors: The financial health, management, and business model of a company can also impact its stock's standard deviation.
- Economic Indicators: Factors like interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth can influence stock market volatility and, subsequently, standard deviation.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of these factors on standard deviation, let's consider a few case studies:
- Tech Sector during the Dot-com Bubble: During the late 1990s, the tech sector experienced a surge in stock prices, followed by a sharp correction. This volatility contributed to a higher standard deviation in the tech sector during that period.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic led to significant market volatility, with US stocks experiencing record-high standard deviation as investors grappled with economic uncertainty.
- Financial Crisis of 2008: The 2008 financial crisis triggered a global financial downturn, resulting in higher standard deviation across various sectors and industries.
Conclusion
Understanding the average standard deviation of US stocks is essential for investors looking to navigate the volatile market. By considering market conditions, sector and industry risks, company-specific factors, and economic indicators, investors can make more informed decisions and manage their risk effectively.
new york stock exchange