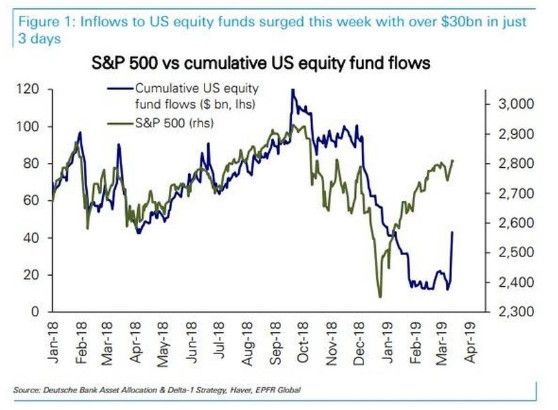
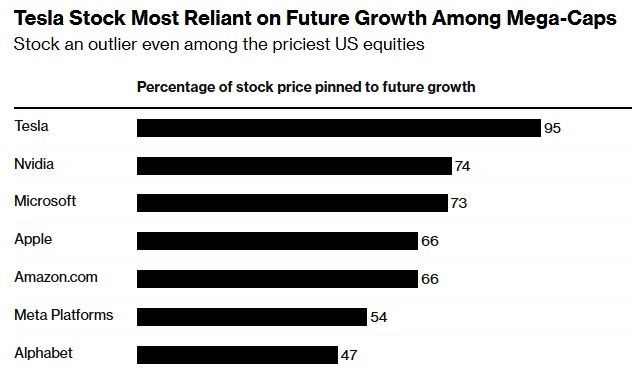
New York Stock Exchange: A Comprehensive Overview
author:US stockS -New(52)York(46)Exchange(39)Stock(238)Compre(11)
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) stands as a beacon of financial markets, providing a platform for companies to raise capital and investors to grow their wealth. As one of the most significant stock exchanges in the world, the NYSE has played a pivotal role in shaping the global financial landscape. In this article, we delve into the history, operations, and impact of the New York Stock Exchange.
The History of the NYSE
Established in 1792, the NYSE is one of the oldest stock exchanges in the United States. The exchange's origins can be traced back to the Buttonwood Agreement, where 24 brokers gathered under a buttonwood tree to form the New York Stock & Exchange Board. Over the years, the NYSE has evolved and expanded, becoming a global hub for financial transactions.
Notable Milestones:
- 1792: The Buttonwood Agreement was signed, establishing the New York Stock & Exchange Board.
- 1817: The exchange was incorporated as the New York Stock Exchange.
- 1863: The exchange moved to its current location, 11 Wall Street.
- 1971: The trading floor was computerized, marking a significant shift in operations.
- 2007: The NYSE acquired the American Stock Exchange (AMEX), creating a more robust and diversified trading platform.
Operations of the NYSE
The NYSE operates as a public entity, regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The exchange facilitates the buying and selling of stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. Here's a breakdown of its key operations:
Trading: The NYSE operates on an auction-based system, where buyers and sellers meet to execute trades. The trading floor, also known as "The Pit," is where many of these transactions occur.
Listing: Companies looking to go public must meet specific criteria to list their shares on the NYSE. These criteria include financial performance, governance, and market capitalization.
Market Data: The NYSE provides real-time market data, including stock prices, trading volumes, and other financial metrics.
Impact of the NYSE
The New York Stock Exchange has had a profound impact on the global financial system. Here are some of its key contributions:
Capital Formation: The NYSE has facilitated the capital formation process, allowing companies to raise funds for expansion and innovation.
Market Efficiency: The exchange has improved market efficiency by providing a centralized platform for trading, ensuring transparency and liquidity.
Global Influence: The NYSE has played a crucial role in shaping global financial markets, influencing policies and practices worldwide.
Case Studies:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL): Apple went public on the NYSE in 1980, raising $18 million. Since then, the company has become one of the most valuable and influential companies in the world.
- Facebook Inc. (FB): Facebook listed on the NYSE in 2012, raising $16 billion. The listing was one of the largest in history and marked the beginning of Facebook's journey as a public company.
Conclusion
The New York Stock Exchange has been a cornerstone of the global financial system for over two centuries. Its history, operations, and impact have shaped the way we perceive and interact with financial markets today. As the world continues to evolve, the NYSE remains a vital institution, connecting companies and investors in an ever-changing financial landscape.
dow and nasdaq today