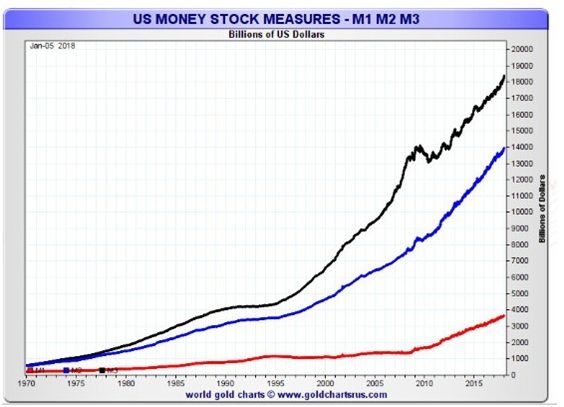
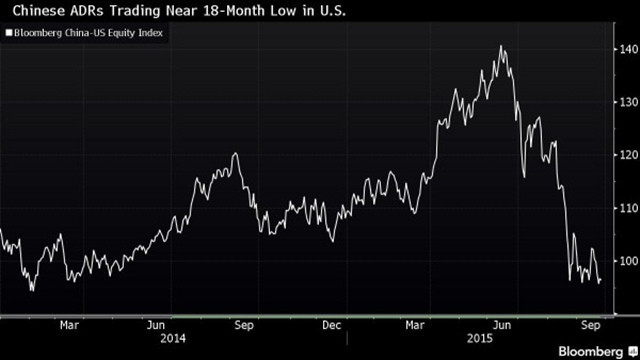
Chinese vs. US Stock Market Presentations: A Comparative Analysis
author:US stockS -
Understanding the Chinese Stock Market
The Chinese stock market, often referred to as the "A-share" market, has been a focal point for investors and financial experts worldwide. With its unique structure and regulatory environment, understanding the nuances of this market is crucial. In this section, we will explore the key aspects that differentiate the Chinese stock market from its American counterpart.
Regulatory Framework
The Chinese stock market operates under a different regulatory framework compared to the United States. In China, the State Administration of Exchange (SAFE) and the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) play a pivotal role in overseeing the market. These regulatory bodies implement rules that differ from those in the US, such as the requirement for a minimum investment threshold for foreign investors.

Market Structure
The Chinese stock market consists of two primary exchanges: the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE). The SSE, established in 1990, is the oldest and largest of the two, while the SZSE, founded in 1991, is known for its technology and growth-oriented companies. In contrast, the US stock market is dominated by the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq, which are renowned for their broad and diverse range of companies.
Sector Distribution
Another notable difference between the Chinese and US stock markets lies in the sector distribution. The Chinese market has a significant weight in sectors such as energy, materials, and financials, which can be attributed to the country's heavy reliance on state-owned enterprises. Conversely, the US market is more diversified, with significant exposure to technology, healthcare, and consumer discretionary sectors.
Investment Strategies
Investing in the Chinese stock market requires a different approach compared to the US market. Due to the market's unique characteristics, investors often focus on macroeconomic indicators and political stability when evaluating investments. On the other hand, the US market emphasizes fundamentals analysis, including financial statements, management quality, and growth prospects.
Case Study: Alibaba vs. Amazon
A prime example of the difference between Chinese and US stock market presentations is the comparison of Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. (BABA) and Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN). Both companies operate in the e-commerce space, but their market performance and investor sentiment differ significantly.
Alibaba
Alibaba, listed on the New York Stock Exchange, has seen significant growth in its stock price since its initial public offering in 2014. Despite facing regulatory challenges in China, the company's focus on e-commerce and cloud computing has driven its success. Investors in the US market have generally favored Alibaba due to its potential for growth and innovation.
Amazon
In contrast, Amazon, listed on the Nasdaq, has a more diversified business model, encompassing e-commerce, cloud computing, and streaming services. While the company has faced similar regulatory challenges in the US, its market presence and brand recognition have contributed to a strong investor sentiment. Amazon's stock price has also experienced substantial growth, although at a slower pace compared to Alibaba.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the Chinese and US stock markets is essential for investors looking to expand their global investment portfolios. By analyzing the regulatory framework, market structure, sector distribution, and investment strategies, investors can make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital. As the global economy continues to evolve, staying abreast of these differences will be crucial for long-term investment success.
dow and nasdaq today