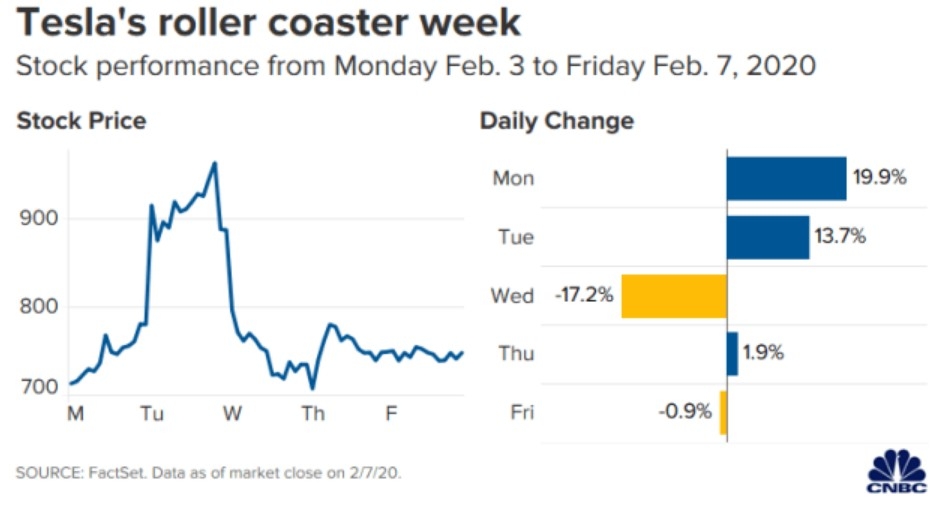
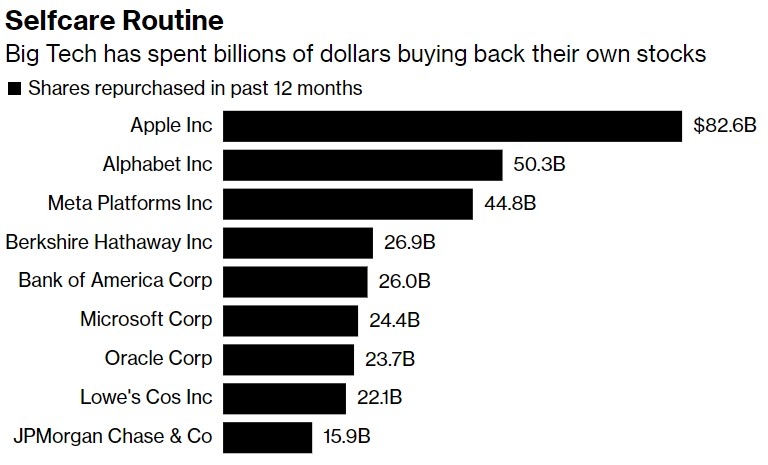
Understanding the US Stock Market Average PE Ratio
author:US stockS -
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, one key metric that investors closely monitor is the US stock market average PE ratio. The Price-to-Earnings (PE) ratio is a valuation metric that compares the price of a company's stock to its per-share earnings. This article delves into what the US stock market average PE ratio signifies, its implications for investors, and how it has changed over the years.
What is the US Stock Market Average PE Ratio?
The US stock market average PE ratio is a measure of the overall valuation of the stock market. It is calculated by dividing the total market capitalization of all stocks in the US by the total earnings of all companies in the S&P 500 index. This ratio provides a snapshot of how expensive or cheap the overall stock market is at any given time.
Historical Context
Over the past few decades, the US stock market average PE ratio has fluctuated significantly. In the 1990s, during the dot-com boom, the PE ratio reached as high as 45. In contrast, during the financial crisis of 2008, the PE ratio dropped to around 12. Historically, the average PE ratio has been around 15 to 20.
Implications for Investors
Understanding the PE ratio is crucial for investors as it helps them gauge the overall market sentiment and make informed investment decisions. A higher PE ratio indicates that the market is expensive, suggesting that investors are willing to pay more for earnings. Conversely, a lower PE ratio suggests that the market is undervalued, potentially offering better long-term investment opportunities.
Current State of the US Stock Market Average PE Ratio
As of [current date], the US stock market average PE ratio stands at [current PE ratio]. This figure provides insight into the current market sentiment. If the PE ratio is above the historical average, it may indicate that the market is overvalued, and investors may want to exercise caution. Conversely, if the PE ratio is below the historical average, it may suggest that the market is undervalued, presenting potential opportunities for long-term investors.
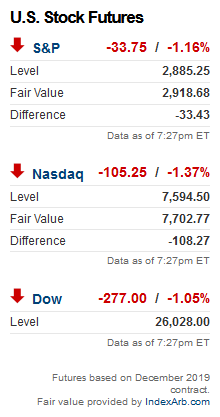
Case Study: The 1990s Dot-Com Boom
One of the most notable periods in the history of the US stock market average PE ratio was the 1990s dot-com boom. During this time, the PE ratio skyrocketed to over 45, driven by the rapid growth of technology companies. However, this bubble eventually burst, leading to significant declines in stock prices and a sharp drop in the PE ratio. This case study highlights the importance of understanding market valuations and the potential risks associated with overvalued markets.
Conclusion
The US stock market average PE ratio is a vital metric for investors seeking to understand the overall valuation of the market. By analyzing this ratio, investors can gauge market sentiment and make informed decisions. While the current PE ratio may suggest a range of possibilities, it is crucial to consider historical context and potential risks before making any investment decisions.
us stock market today live cha