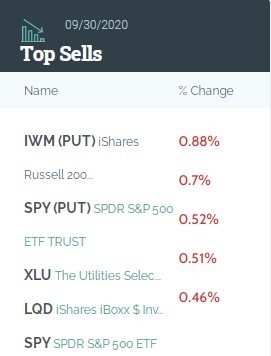
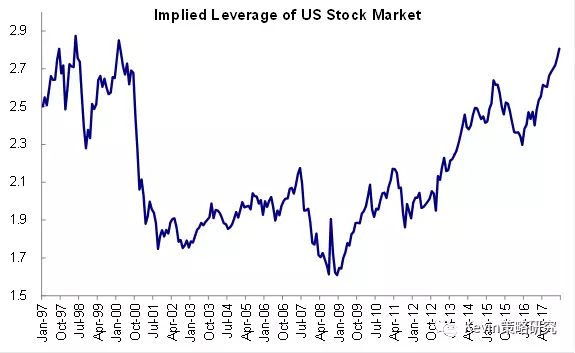
Understanding the US Stock Margin Ratio: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the world of stock trading, the margin ratio plays a crucial role in determining the leverage available to investors. For those unfamiliar with this term, the US stock margin ratio refers to the proportion of equity an investor must maintain in their margin account to cover any potential losses. This article delves into the intricacies of the US stock margin ratio, its significance, and how it impacts investors' trading strategies.
What is the US Stock Margin Ratio?
The US stock margin ratio is a regulatory measure implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to mitigate the risk of trading on margin. It is calculated by dividing the equity in the margin account by the total debt in the account. The equity includes the cash balance, the market value of securities, and any other funds that are not borrowed. The debt, on the other hand, represents the amount of money borrowed to purchase stocks.
How is the US Stock Margin Ratio Calculated?
The formula for calculating the US stock margin ratio is as follows:
Margin Ratio = (Equity / Total Debt) x 100
For example, if an investor has
Significance of the US Stock Margin Ratio
Risk Management: The margin ratio serves as a tool for risk management. By maintaining a certain level of equity, investors can avoid margin calls, which occur when the margin ratio falls below a certain threshold set by the brokerage firm.
Leverage: A higher margin ratio indicates a lower level of leverage, which means the investor is using less borrowed capital to trade. This can help mitigate the risk of large losses.
Regulatory Compliance: The margin ratio is a regulatory requirement, and failing to maintain the required level can result in penalties or restrictions on trading.
Impact on Trading Strategies
The US stock margin ratio can significantly impact trading strategies. Here are a few key points to consider:
Leverage: A higher margin ratio means less leverage, which can be beneficial for conservative traders who prefer to minimize risk.
Risk Management: By monitoring the margin ratio, traders can adjust their positions to avoid margin calls and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Market Conditions: In volatile markets, maintaining a higher margin ratio can help mitigate the risk of significant losses.
Case Study: Impact of Margin Ratio on Trading Performance
Consider two traders, Alex and Jamie, who both invest $10,000 in a stock. Alex maintains a margin ratio of 50%, while Jamie maintains a margin ratio of 20%.
Alex: By maintaining a lower margin ratio, Alex is using less borrowed capital, which reduces the risk of large losses. In a volatile market, this can be a significant advantage.
Jamie: Jamie is using more leverage, which can amplify gains but also increase the risk of significant losses. In a volatile market, this can be detrimental to Jamie's trading performance.
Conclusion
The US stock margin ratio is a critical factor in risk management and trading strategies. By understanding and monitoring this ratio, investors can make informed decisions and minimize the risk of margin calls and regulatory penalties. Whether you are a conservative or aggressive trader, maintaining an appropriate margin ratio is essential for long-term success in the stock market.
us stock market today live cha