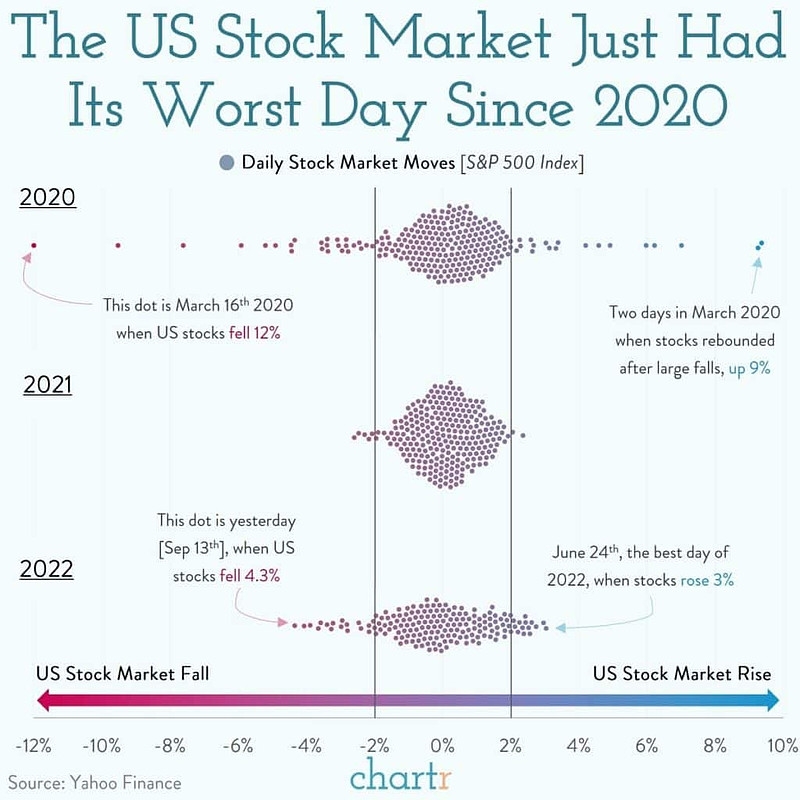
Understanding the US Stock Circuit Breaker: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the volatile world of stock markets, the US Stock Circuit Breaker serves as a crucial safety mechanism. This article delves into the concept, its history, and its significance in maintaining market stability. Circuit breakers are designed to pause trading during periods of extreme market volatility, thereby protecting investors and ensuring a fair and orderly market.
What is the US Stock Circuit Breaker?
The US Stock Circuit Breaker is a regulatory measure implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). It aims to prevent extreme market movements, often referred to as "flash crashes," which can cause significant financial damage. The circuit breaker is designed to halt trading on major stock exchanges when the market experiences sudden, extreme drops or rises in prices.
History of the Circuit Breaker
The concept of a circuit breaker was introduced in response to the Black Monday crash of 1987, where the stock market experienced a dramatic and sudden drop. The SEC implemented the Circuit Breaker Rule in 1988, which required exchanges to halt trading for a short period during periods of extreme market volatility.
How Does the Circuit Breaker Work?
The US Stock Circuit Breaker operates based on a trigger point, which is determined by the Standard & Poor's 500 Index (S&P 500). If the S&P 500 index falls by a predetermined percentage within a specified time frame, trading on major stock exchanges is halted for a short period. The trigger points are as follows:
- 7% decline: Trading is halted for 15 minutes.
- 13% decline: Trading is halted for an additional 15 minutes.
- 20% decline: Trading is halted until the opening of the next trading day.
This halt in trading allows market participants to assess the situation and make informed decisions, reducing the likelihood of further market instability.
Significance of the Circuit Breaker
The US Stock Circuit Breaker plays a vital role in maintaining market stability. By halting trading during extreme market movements, the circuit breaker helps prevent panic selling and allows investors to react more calmly. This mechanism also protects investors from potential financial loss and ensures a fair and orderly market.
Case Studies
One notable example of the circuit breaker in action is the Flash Crash of 2010. On May 6, 2010, the S&P 500 experienced a sudden and dramatic drop of over 5% within minutes. The circuit breaker triggered, halting trading for 20 minutes. This halt allowed market participants to stabilize the market, and trading resumed with a more orderly market.
Conclusion
The US Stock Circuit Breaker is a critical regulatory tool that helps maintain market stability during periods of extreme volatility. By halting trading when necessary, the circuit breaker protects investors and ensures a fair and orderly market. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for anyone involved in the stock market, as it helps mitigate the risks associated with market instability.
us stock market today live cha