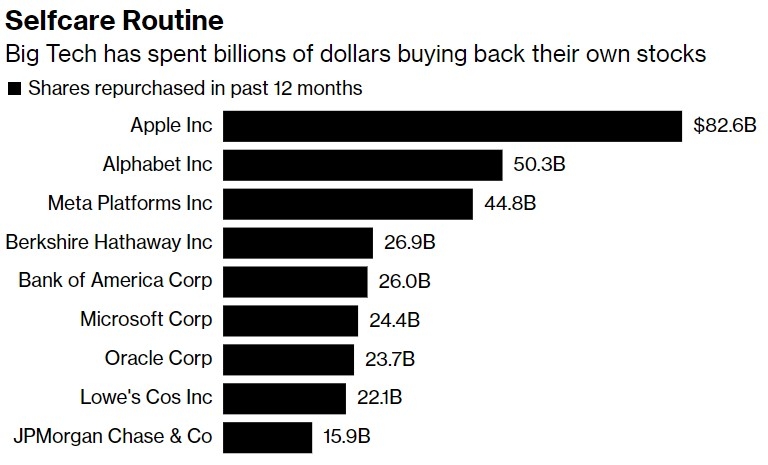
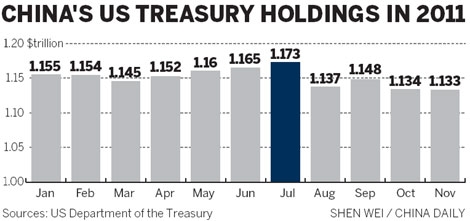
Understanding the Dynamics of US Stock and Bonds
author:US stockS -
In the vast world of financial markets, US stocks and bonds play a pivotal role. For investors looking to diversify their portfolios, understanding the intricacies of these instruments is crucial. This article delves into the key aspects of US stocks and bonds, highlighting their differences, benefits, and risks.
Stocks: Ownership and Growth Potential
When you invest in stocks, you are essentially purchasing a share of a company. This makes you a partial owner, granting you voting rights in certain corporate decisions. The primary objective of investing in stocks is to earn a return on your investment through capital appreciation and dividends.
Key Points About Stocks:
- Capital Appreciation: If the company performs well, its stock price may increase, allowing you to sell your shares at a higher price and earn a profit.
- Dividends: Some companies distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. This can provide a regular income stream.
- Risk: Stock prices can be volatile, and there's no guarantee that your investment will increase in value.
Bonds: Stability and Income
On the other hand, bonds are debt instruments issued by companies or governments to raise capital. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of your principal amount at maturity.
Key Points About Bonds:
- Interest Payments: Bonds pay interest at regular intervals, typically semi-annually or annually, providing a stable income stream.
- Maturity: Bonds have a fixed maturity date, after which the issuer repays the principal amount.
- Risk: Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks, but their returns are typically lower.
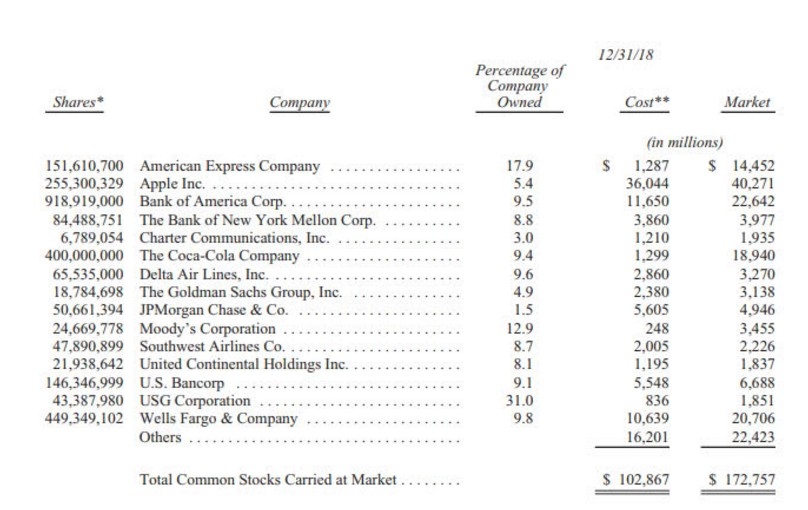
Differences Between Stocks and Bonds
While both stocks and bonds are popular investment options, they differ significantly in terms of risk, return, and ownership.
- Risk: Stocks are generally considered riskier than bonds because their prices can fluctuate widely. Bonds, on the other hand, are considered less risky as they provide a fixed income stream and a guaranteed return of principal at maturity.
- Return: Stocks have the potential to offer higher returns than bonds, but they also come with higher risk. Bonds typically provide a lower return but are more stable.
- Ownership: As mentioned earlier, stocks provide ownership in the company, while bonds do not.
Case Study: Apple Inc.
To illustrate the differences between stocks and bonds, let's consider the case of Apple Inc. (AAPL).
- Stocks: Apple Inc. is a well-known technology company that has seen significant growth over the years. As a stockholder, you would benefit from the company's growth and potentially earn a high return on your investment. However, stock prices can be volatile, and there's no guarantee of profit.
- Bonds: Apple Inc. also issued bonds to raise capital. These bonds provided a stable income stream to investors, but the returns were lower than what they would have earned from stock investments.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of US stocks and bonds is essential for investors looking to diversify their portfolios. While stocks offer the potential for higher returns, they come with higher risk. Bonds, on the other hand, provide stability and a fixed income stream. By carefully considering your investment goals and risk tolerance, you can make informed decisions about where to allocate your capital.
us stock market today