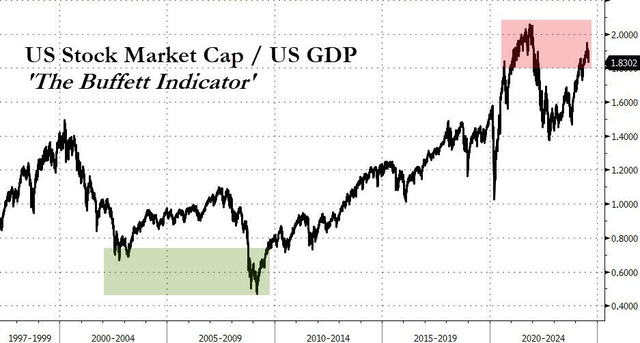
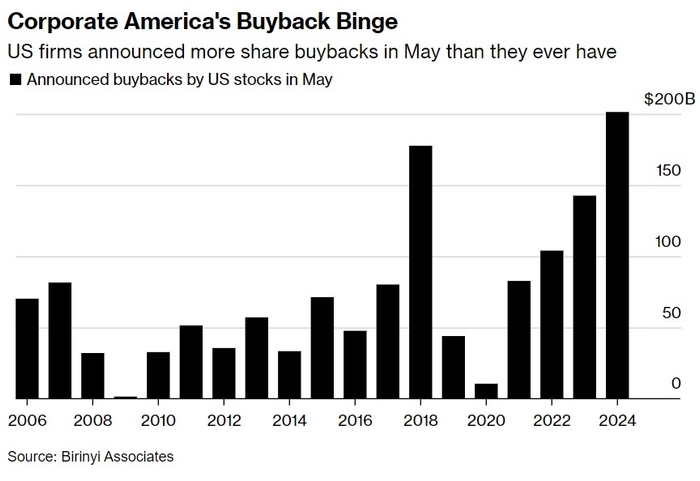
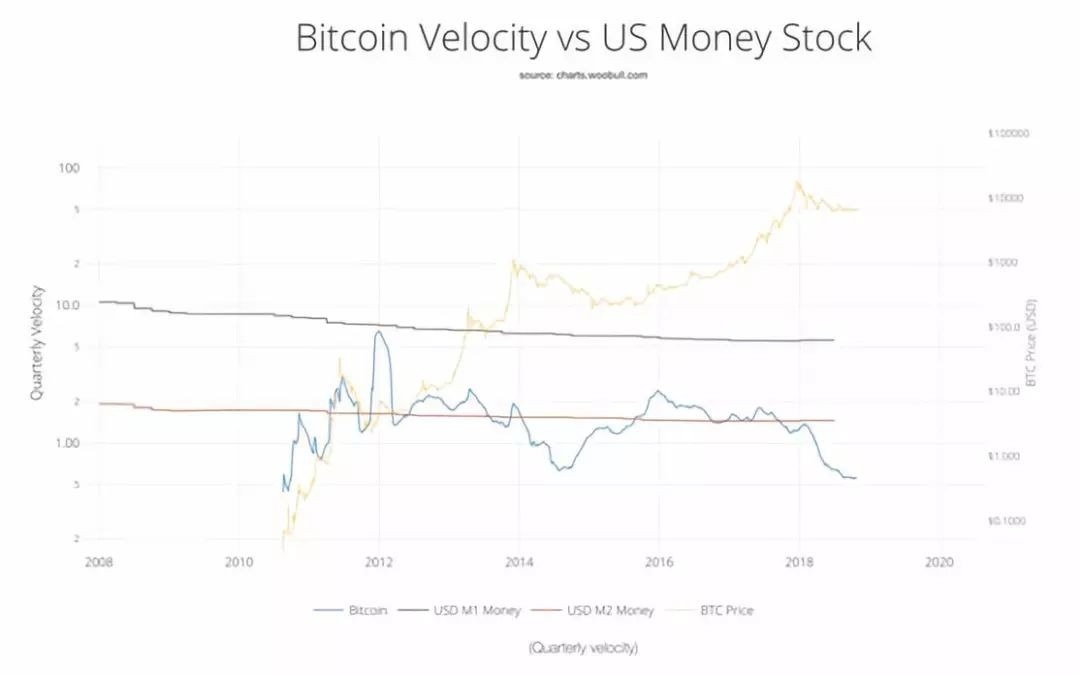
Understanding Non-US Stock Merger Consideration: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the world of international business, understanding the intricacies of non-US stock merger consideration is crucial for companies seeking global expansion. This guide delves into the key aspects of non-US stock mergers, including valuation, regulatory considerations, and legal implications.
Valuation of Non-US Stocks
Valuing non-US stocks in a merger can be complex due to differences in accounting standards and market conditions. Companies must consider several factors to ensure a fair and accurate valuation, including:
- Local Market Conditions: Understanding the economic and political landscape of the target country is essential. Factors such as inflation, currency exchange rates, and market volatility can significantly impact valuation.
- Accounting Standards: Differences in accounting standards between the US and the target country can lead to discrepancies in financial reporting. It is crucial to have a clear understanding of these differences to ensure accurate valuation.
- Future Cash Flows: Estimating the future cash flows of the non-US company is vital for determining its value. Companies must consider factors such as market growth, competitive landscape, and regulatory changes.
Regulatory Considerations
Mergers involving non-US stocks must comply with various regulatory requirements, including:
- Antitrust Laws: Both the US and the target country may have antitrust laws that need to be considered. Companies must ensure that the merger does not lead to anti-competitive practices.
- Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA): If the non-US company operates in a country with high corruption risks, the FCPA may apply. Companies must comply with FCPA requirements to avoid legal penalties.
- Local Regulatory Framework: Each country has its own set of regulations governing mergers and acquisitions. Companies must navigate these regulations to ensure a successful transaction.
Legal Implications
Legal implications of non-US stock mergers can be complex and vary depending on the jurisdiction. Key considerations include:
- Shareholder Approval: Companies must obtain approval from shareholders of both the US and non-US companies. This process may require compliance with local corporate governance rules.
- Contractual Agreements: Mergers typically involve complex contractual agreements, including non-compete clauses and intellectual property rights. Ensuring that these agreements are legally enforceable is crucial.
- Cross-border Taxation: Mergers involving non-US stocks may have tax implications for both companies. Understanding the tax laws of both jurisdictions is essential to minimize tax liabilities.
Case Study: Facebook’s Acquisition of WhatsApp
One notable example of a non-US stock merger is Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp in 2014. The deal, valued at $19 billion, highlighted several key considerations for non-US stock mergers:
- Valuation: Facebook conducted a thorough valuation of WhatsApp, considering its user base, growth potential, and market conditions.
- Regulatory Approval: The acquisition received approval from antitrust authorities in both the US and India, where WhatsApp had a significant user base.
- Legal Implications: Facebook navigated the legal complexities of the deal, including shareholder approval and contractual agreements.
Conclusion
Understanding non-US stock merger consideration is essential for companies seeking global expansion. By considering valuation, regulatory requirements, and legal implications, companies can navigate the complexities of international mergers and achieve successful outcomes.

us stock market today