Impact of US National Debt on Stock Market
author:US stockS -
The United States, as the world's largest economy, has accumulated a significant national debt over the years. This debt has raised concerns among investors and economists alike, particularly regarding its potential impact on the stock market. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between the national debt and the stock market, exploring how the two are interconnected and the potential risks and opportunities that arise from this relationship.
Understanding the National Debt
The national debt refers to the total amount of money that the federal government owes to its creditors. This debt has been accumulating over the years due to various factors, including budget deficits, wars, and economic stimulus programs. As of 2021, the national debt stands at over $28 trillion, a figure that continues to grow.
The Debt-Growth Relationship
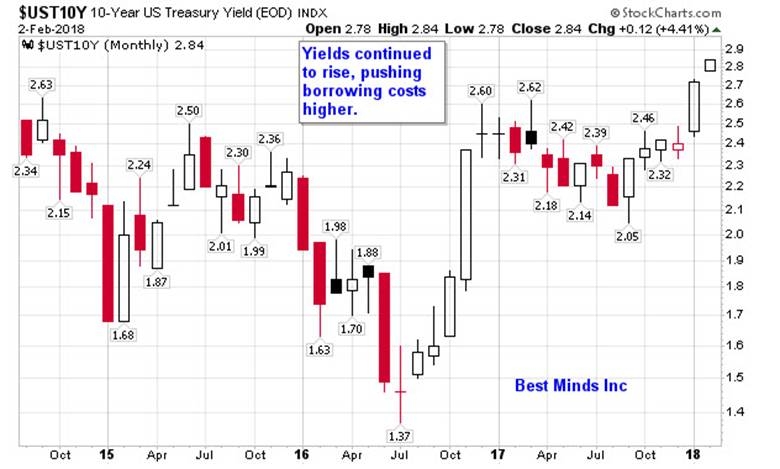
One of the most significant concerns about the national debt is its potential impact on economic growth. When the government borrows money, it typically does so by issuing Treasury bonds and notes. These securities are purchased by investors, including individuals, institutions, and foreign governments. As the debt increases, the government must issue more securities, which can lead to higher interest rates.
Higher interest rates can have a negative impact on economic growth. When interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase for businesses and consumers, which can lead to reduced investment and consumption. This, in turn, can slow down economic growth and potentially lead to a recession.
Impact on the Stock Market
The stock market is sensitive to changes in the economy and interest rates. When the national debt increases, it can have several effects on the stock market:
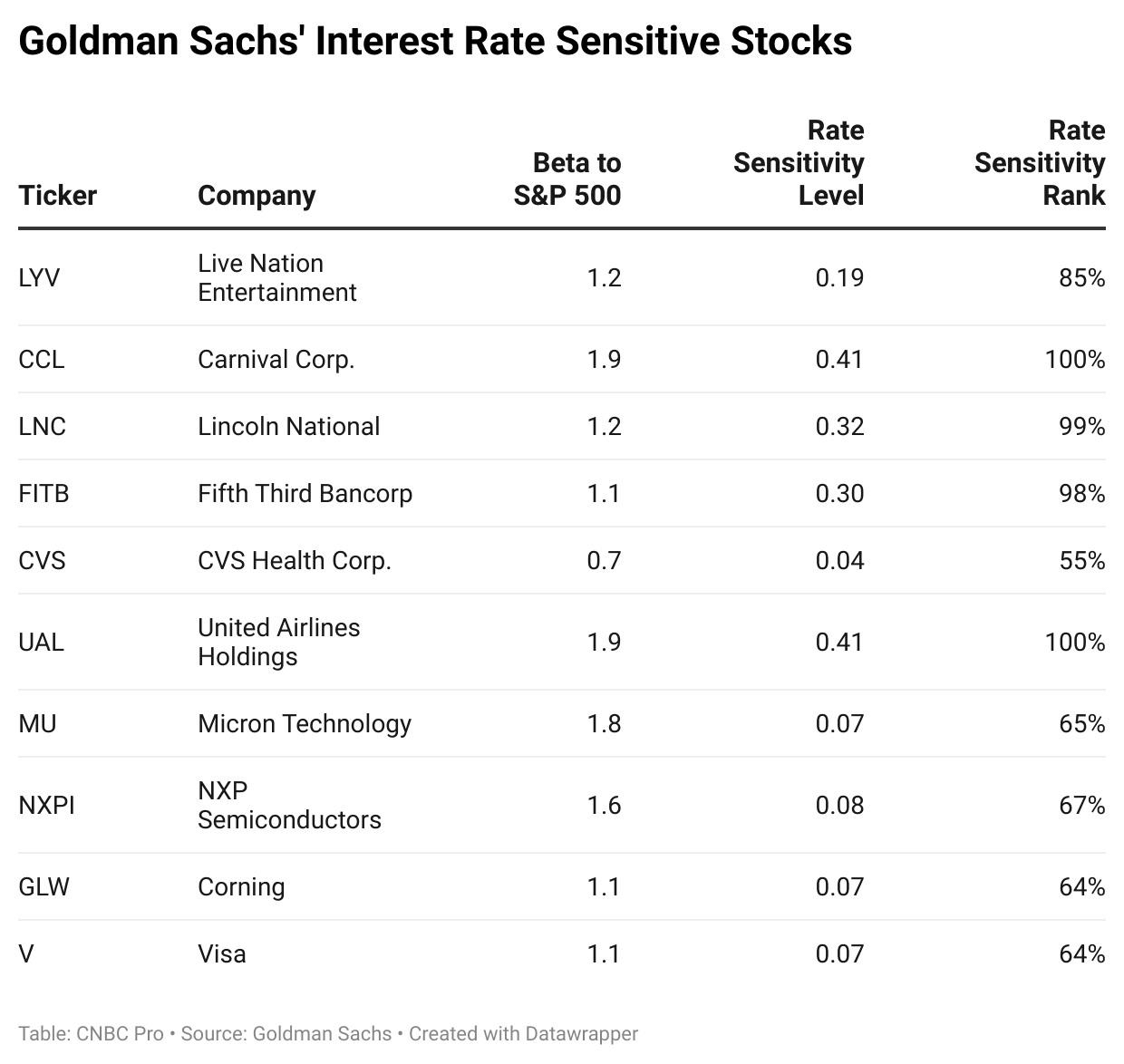
- Higher Interest Rates: As mentioned earlier, higher interest rates can lead to reduced economic growth. This can negatively impact corporate earnings, which are a key driver of stock prices. Additionally, higher interest rates can make bonds more attractive to investors, leading to a shift in capital away from stocks.
- Market Volatility: The national debt can also contribute to market volatility. When investors become concerned about the government's ability to manage its debt, they may sell off stocks, leading to increased market volatility.
- Investor Sentiment: The national debt can also influence investor sentiment. If investors believe that the government's debt is unsustainable, they may become more cautious and risk-averse, leading to a sell-off in stocks.
Case Studies
Several case studies have highlighted the relationship between the national debt and the stock market. For example, during the 1980s, the national debt increased significantly under President Ronald Reagan. This period was characterized by high inflation and interest rates, which led to a bear market in the stock market. Similarly, during the 2008 financial crisis, the national debt increased as the government implemented various stimulus programs. While the stock market initially fell, it eventually recovered as the economy stabilized.
Conclusion
The relationship between the national debt and the stock market is complex and multifaceted. While the national debt can have a negative impact on the stock market through higher interest rates and market volatility, it can also present opportunities for investors. As always, it is crucial for investors to stay informed and make informed decisions based on their own risk tolerance and investment goals.
new york stock exchange