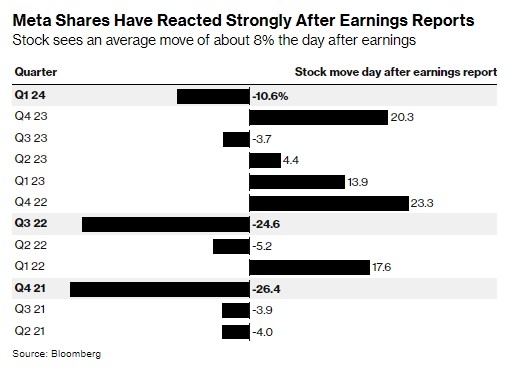
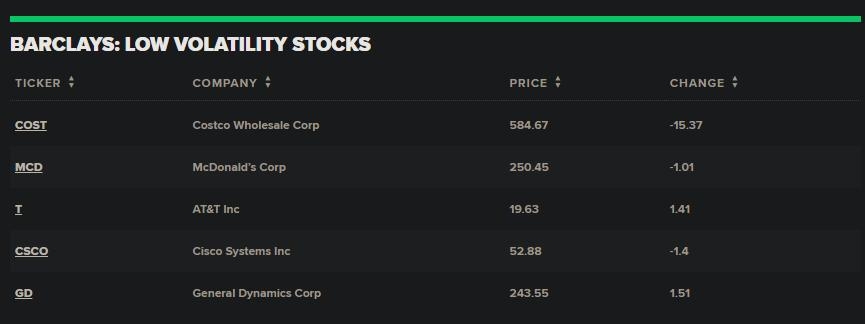
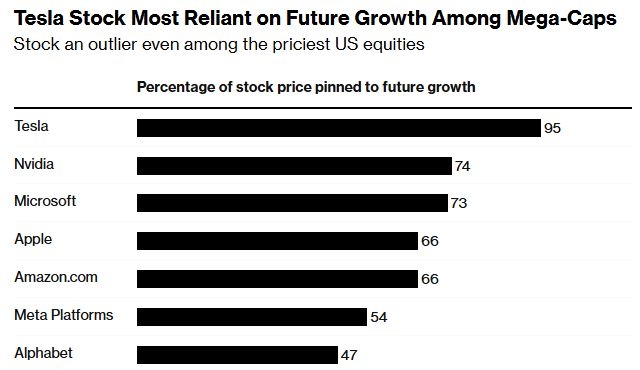
US Bonds vs. US Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the world of investing, two of the most popular assets are US bonds and US stocks. Both offer unique benefits and risks, making it essential for investors to understand the differences between them. This article will explore the key aspects of US bonds and US stocks, including their characteristics, potential returns, and risk factors. By the end, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your investment strategy.
Understanding US Bonds
US bonds are debt securities issued by the US government or corporations. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of your principal amount at maturity. Here are some key characteristics of US bonds:
- Low Risk: US government bonds are considered one of the safest investments due to the backing of the US government. Corporate bonds may have higher risk but typically offer higher yields.
- Income: Bonds provide a fixed income stream in the form of regular interest payments, which can be an attractive option for investors seeking stable income.
- Liquidity: Bonds are generally more liquid than stocks, meaning they can be bought and sold relatively easily.
Understanding US Stocks
US stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy stocks, you are purchasing a share of the company's assets and profits. Here are some key characteristics of US stocks:
- Potential for High Returns: Stocks have historically provided higher returns than bonds over the long term, although they come with higher risk.
- Growth: Investors can benefit from the company's growth and potential increase in share price.
- Dividends: Some companies distribute dividends to shareholders, providing an additional income stream.
Comparing US Bonds and US Stocks
Now that we have a basic understanding of US bonds and US stocks, let's compare them on several key factors:
- Risk: US bonds are generally less risky than stocks, but they also offer lower returns. Investors who prioritize stability and income may prefer bonds, while those seeking higher returns may lean towards stocks.
- Income: Bonds provide a fixed income stream, while stocks may offer dividends, which can be more variable.
- Liquidity: Both bonds and stocks are generally liquid, but bonds may have slightly higher liquidity due to their more standardized nature.
- Diversification: Investing in both bonds and stocks can help diversify your portfolio and reduce risk.
Case Studies
To illustrate the differences between US bonds and US stocks, let's consider two case studies:
- Case Study 1: An investor buys a US government bond with a 10-year maturity and a 3% interest rate. Over the 10-year period, the investor receives regular interest payments and the principal amount at maturity, resulting in a stable, predictable return.
- Case Study 2: An investor buys shares of a technology company with a promising future. Over the next few years, the company experiences significant growth, and the share price increases significantly, resulting in a substantial return for the investor.
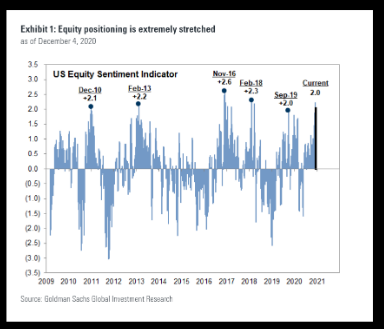
In conclusion, both US bonds and US stocks offer unique benefits and risks. Investors must carefully consider their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon when choosing between the two. By understanding the key differences between US bonds and US stocks, you can make informed decisions to build a well-diversified investment portfolio.
dow and nasdaq today