How Much to Allocate to US Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
Are you considering adding US stocks to your investment portfolio? If so, one of the most crucial questions you need to answer is: how much should you allocate to US stocks? This guide will help you understand the factors to consider when determining the appropriate allocation for US stocks in your investment strategy.
Understanding Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of dividing your investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. The goal of asset allocation is to balance risk and return, ensuring that your portfolio aligns with your financial objectives.
Factors to Consider When Allocating to US Stocks
Risk Tolerance: Your risk tolerance is a critical factor in determining how much you should allocate to US stocks. Generally, stocks are considered riskier than bonds and cash, as their prices can fluctuate significantly. If you have a higher risk tolerance, you may allocate a larger portion of your portfolio to US stocks. Conversely, if you prefer lower risk, you may want to allocate a smaller portion.
Investment Goals: Your investment goals will also influence your allocation. Are you investing for long-term growth, such as retirement, or are you seeking short-term income? If you are investing for long-term growth, you may allocate a larger portion to US stocks, as they tend to offer higher returns over the long term. However, if you are seeking short-term income, you may want to allocate a smaller portion to US stocks and focus on more stable investments, such as bonds.
Diversification: Diversification is key to managing risk in your investment portfolio. By allocating your investments across various sectors and industries, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio. Ensure that your US stock allocation is well-diversified to mitigate risk.
Market Conditions: Keep an eye on the market conditions when determining your US stock allocation. If the market is experiencing a downturn, you may want to allocate a smaller portion to US stocks to protect your portfolio. Conversely, if the market is performing well, you may consider increasing your allocation to US stocks.
Economic Factors: Economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, can also influence your US stock allocation. For example, if interest rates are low, stocks may offer better returns compared to bonds. Conversely, if inflation is high, stocks may be more volatile.
Case Study: The 2008 Financial Crisis
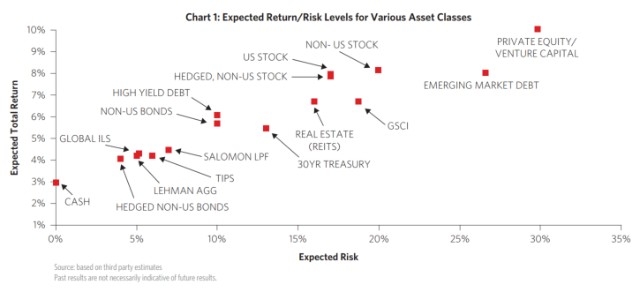
One example of how market conditions can impact your US stock allocation is the 2008 financial crisis. During this period, the stock market experienced a significant downturn. Investors who had a higher allocation to US stocks may have experienced substantial losses. However, those who maintained a well-diversified portfolio and had a lower allocation to US stocks may have fared better.
Conclusion
Determining how much to allocate to US stocks requires careful consideration of your risk tolerance, investment goals, diversification strategy, market conditions, and economic factors. By understanding these factors and staying informed about the market, you can make informed decisions about your US stock allocation and create a well-balanced investment portfolio.
dow and nasdaq today